Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a short-term, goal-oriented psychotherapy treatment that takes a hands-on, practical approach to problem-solving.
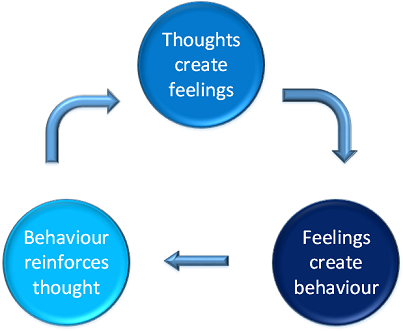
Its goal is to change patterns of thinking or behavior that are behind people’s difficulties, and so change the way they feel.
One important part of CBT is helping clients change their unhelpful thinking and behavior that lead to enduring improvement in their mood and functioning.
History of success
Cognitive behavior therapy is one of the few forms of psychotherapy that has been scientifically tested and found to be effective in hundreds of clinical trials for many different disorders. In contrast to other forms of psychotherapy, cognitive therapy is usually more focused on the present, more limited in duration, and more problem-solving oriented. In addition, patients learn specific skills that they can use for the rest of their lives. These skills involve identifying distorted thinking, modifying beliefs, relating to others in different ways, and changing behaviors.
Techniques
We do lots of problem solving and we borrow from many psychotherapeutic modalities, including dialectical behavior therapy, acceptance and commitment therapy, Gestalt therapy, compassion focused therapy, mindfulness, solution focused therapy, motivational interviewing, positive psychology, interpersonal psychotherapy, and when it comes to personality disorders, psychodynamic psychotherapy.
Cognitive emotional behavioral therapy (CEBT) is a form of CBT developed initially for individuals with eating disorders but now used with a range of problems including anxiety, depression, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and anger problems.


